In this article we will look at introduction to digital forensics which covers computer forensics, cyber forensics and some introduction to digital forensics science.
Introduction
Computer forensics (also known as computer forensic science) is a branch of digital forensic science pertaining to evidence found in computers and digital storage media. The goal of computer forensics is to examine digital media in a forensically sound manner with the aim of identifying, preserving, recovering, analyzing and presenting facts and opinions about the digital information.
Watch the below video for introduction to digital forensics:
Historical Background of Cyberforensics
The earliest computer crimes occurred in 1969 and 1970 when student protesters burned computers at various universities. The Florida Computer Crimes Act (1978) was the first computer law to address computer fraud and intrusion. The focus of computer forensics is to find out digital evidence to establish whether or not a fraud or a crime has been conducted.
Computer forensics deals with proving unauthorized access has taken place while computer security deals with preventing unauthorized access. Typical types of data requested for a digital forensics examination by the law enforcement agencies include:
- investigating email
- website history
- cell phone usage
- VoIP usage
- file access history
- file creation or deletion
- chat history
- account login/logout records
Forensics means a characteristic of evidence that satisfies its suitability for admission as fact and its ability to persuade based upon proof (or high statistical confidence level).
Digital Forensics Science
Watch the below video to learn about digital forensics science:
Digital forensics is the application of analysis techniques to the reliable and unbiased collection, analysis, interpretation and presentation of digital evidence. Computer forensics is the use of analytical and investigative techniques to identify, collect, examine and preserve evidence/information which is magnetically stored or encoded. In general, role of digital forensics is to:
- Uncover and document evidence and leads
- Confirm the evidence discovered in other ways
- Assist in showing a pattern of events
- Connect attack and victim computers
- Reveal an end-to-end path of events leading to a compromise attempt, successful or not
- Extract data that may be hidden, deleted or otherwise not directly available
Typical scenarios involved are:
- Employee Internet abuse
- Data leak/data breach
- Industrial espionage
- Damage assessment
- Criminal fraud and deception cases
- Criminal cases
- Copyright violation
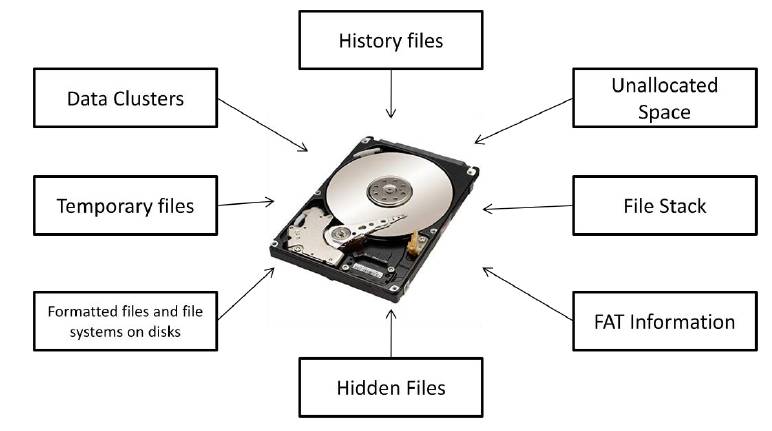
The following figure shows the types of data you see using forensic tools:
Using digital forensics techniques, one can:
- Confirm and clarify evidence otherwise discovered
- Generate investigative leads for follow-up and verification in other ways
- Provide help to verify an intrusion hypothesis
- Eliminate incorrect assumptions

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.



Leave a Reply