In this article we will look at some of the key terms in cybersecurity terminology. This cybersecurity terminology introduces terms like cybercrime, cyberterrorism, cyberspace, etc.
This article is a part of our cyber security tutorial for beginners.
Watch this video to learn about cybercrime definition, its origin and other key terminology related to cybersecurity:
Contents
Cybercrime
There are many definitions for cybercrime. One definition of cybercrime that is recommended is “a crime conducted in which a computer was directly and significantly instrumental.” Other alternative definitions for cybercrime are as follows:
In general, cybercrimes are of two types. They are:
Techno-crime is defined as “a predetermined act against a system or systems, with the intent to copy, steal, prevent access, corrupt or otherwise deface or damage parts of or the complete computer system.”
Techno-vandalism is defined as “the act of brainless defacement of websites and/or other activities, such as copying of files and publicizing their contents publicly, are usually opportunistic in nature.”
Cyberterrorism
The term cybercrime is notorious as it is attached to the word terrorism or terrorist, i.e., cyberterror-ism. Cyberterrorism is defined as “any person, group or organization who, with terrorist intent, utilizes access or aids in accessing a computer or computer network or electronic system or device by any available means, and thereby knowingly engages in or attempts to engage in a terrorist act commits the offence of cyber terrorism.” This term was coined by Barry Collin, a senior research fellow at the Institute for Security and Intelligence in California.
In India and rest of the world, cyberterrorists generally use computer as a tool, target, or both for their criminal activities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information which may lead to heavy loss or damage to the owner of that information. Cyber criminals use methods like phishing, spoofing, pharming, etc for gaining access to the sensitive information.
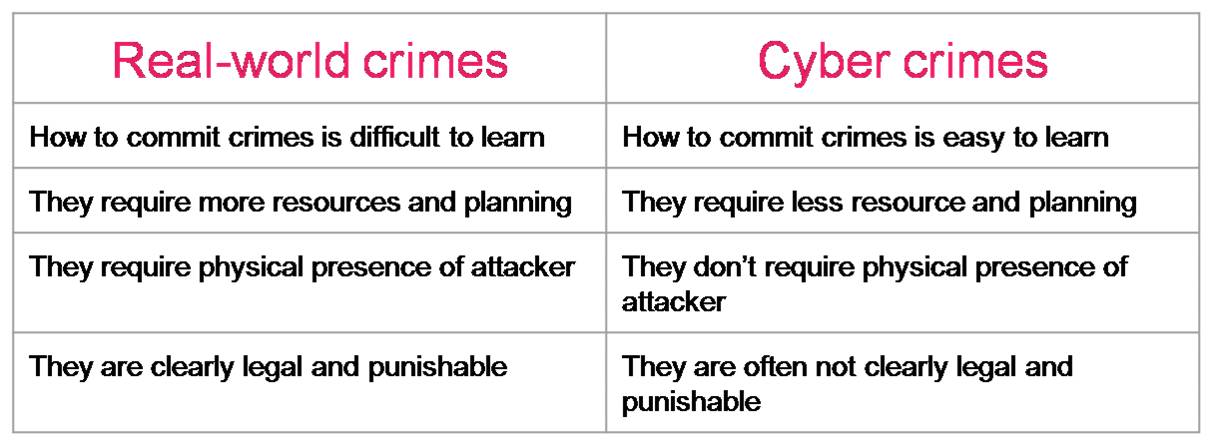
Real-world Crimes vs. Cyber Crimes
Cybercrimes are easier to carry out when compared to real-world crimes. Some of the differences between cybercrimes and real-world crimes are as given below:
Cybernatics
The term cyber had its origin with the word cybernatics which deals with information and its use. Cybernatics is the science that overlaps the fields of neurophysiology, information theory, computing machinery and automation.
Cyberspace
Cyberspace is “a network of computer networks or devices that uses the TCP/IP for communication to facilitate transmission and exchange of data.” The term cyberspace was coined by William Gibson, a science fiction writer, in his Sci-Fi novel, Neuomancer.
Cyber Warfare
Cyber warfare means “information warriors unleashing vicious attacks against opponent’s computer networks, wreaking havoc and paralyzing nations.”
Other Key Terms in Cybersecurity
Real-world example: Consider a real-world example where a person is walking on a bridge with water flowing under it. In this scenario, person might fall into the water due to breakage of the bridge due to cracks. This is a threat to the person. Cracks in the bridge is a vulnerability. After falling into the water the person might die. This is a risk to the person. Cracks can be patched with cement. This counter measure is a control. An enemy of the person walking on the bridge might blow up the bridge to make the person fall into water. Here, blowing the bridge using a bomb is an exploit.
Next let’s learn about cyber crime and information security.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.




Leave a Reply