Aim
Write a java program to demonstrate two-tier client-server model.
Theory
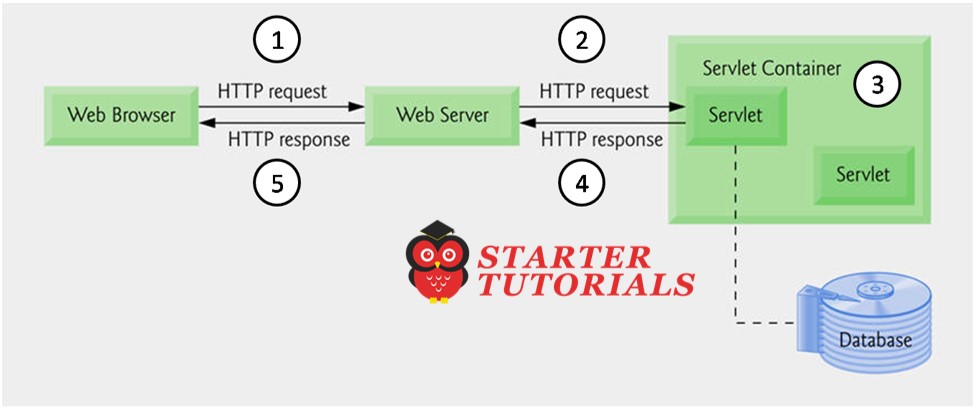
A two-tier client-server architecture consists of a client and a server. The client sends requests to the server and the server takes the request, processes the request and sends a response back. The two-tier client server architecture can be visualized as shown in the figure below:
The client generally sends the request through a web browser like Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox or Opera and views the response (generally a webpage built using HTML/CSS and/or JavaScript) again in the web browser. On the server tier, a server-side programming technology like Servlets can be used to process the requests and send back responses to the client.
Servlets
Servlets is a Java based technology for server-side processing. Other languages or technologies for server-side processing are PHP, JSP, node.js, Perl etc. A servlet is a special Java class which is dynamically loaded on the server and used to generate dynamic content.
Following are the general steps that happen when a client requests a servlet:
- Client sends a HTTP request from web browser containing a URL with servlet.
- Web server receives the request and forwards the request to application server.
- Using information available in xml (deployment descriptor) the servlet container loads the object appropriate servlet class.
- If required, the servlet retrieves data from database, processes it and sends the response back to web server.
- Web server forwards the response back to the client who sent the request.
Above steps can be illustrated as follows:
Servlet API is a set of classes and interfaces that specify a contract between a servlet class and a servlet container. Some examples of servers that provide servlet containers are: Apache Tomcat, Oracle’s WebLogic, IBM’s Websphere, JBoss etc. All the API classes and interfaces are grouped into following packages:
- servlet
- servlet.http
Program
index.html (contains client-side code)
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello Servlet</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="HelloServlet" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="Invoke Servlet!" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
HelloServlet.java (contains server side code)
import java.io.*;
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
{
response.getWriter().write("Hello World!");
}
}
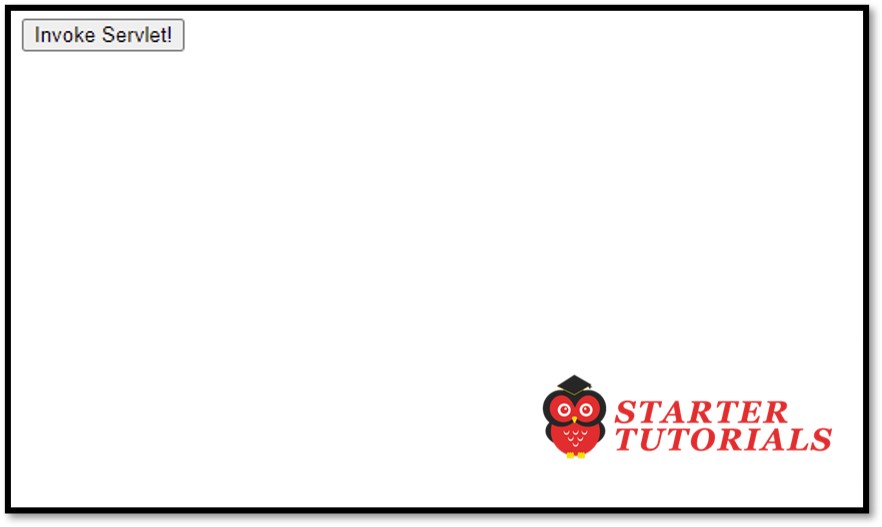
Input and Output
index.html
HelloServlet.java

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.





Leave a Reply